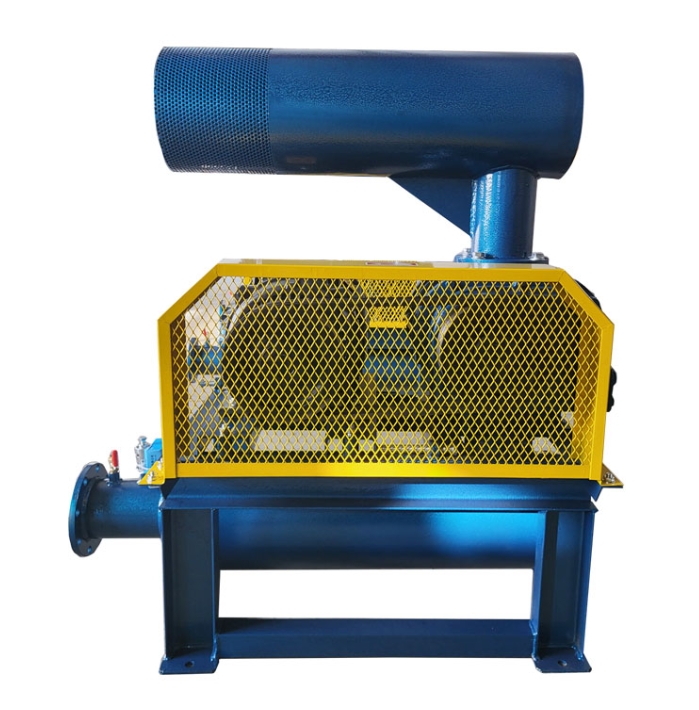
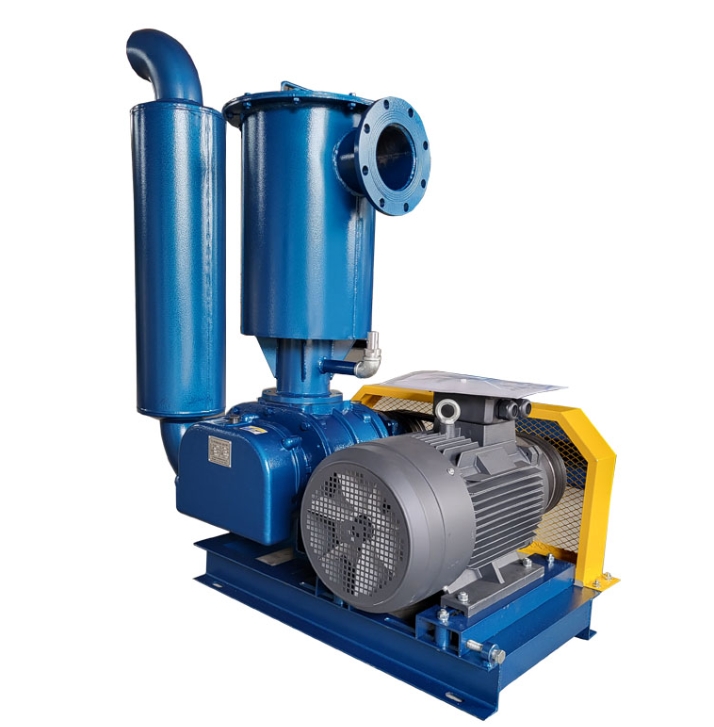
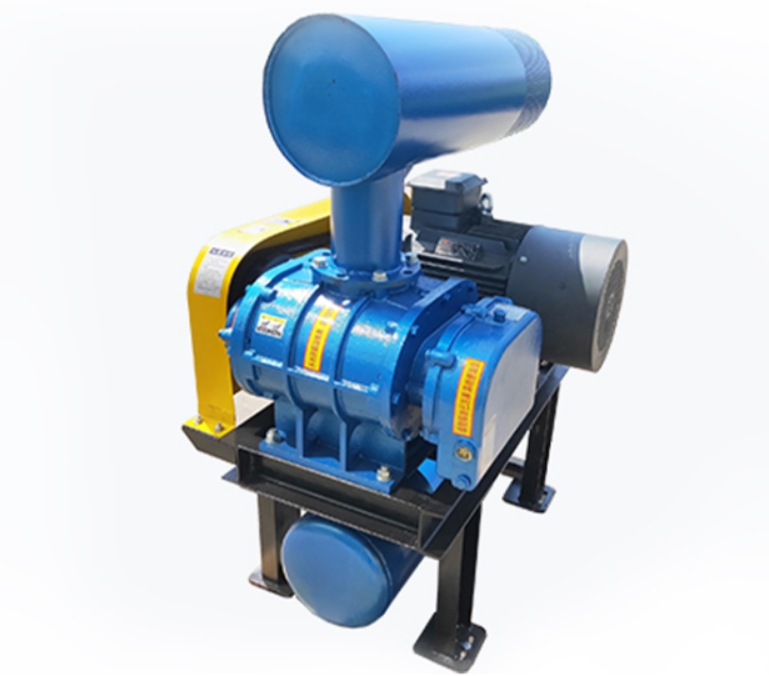
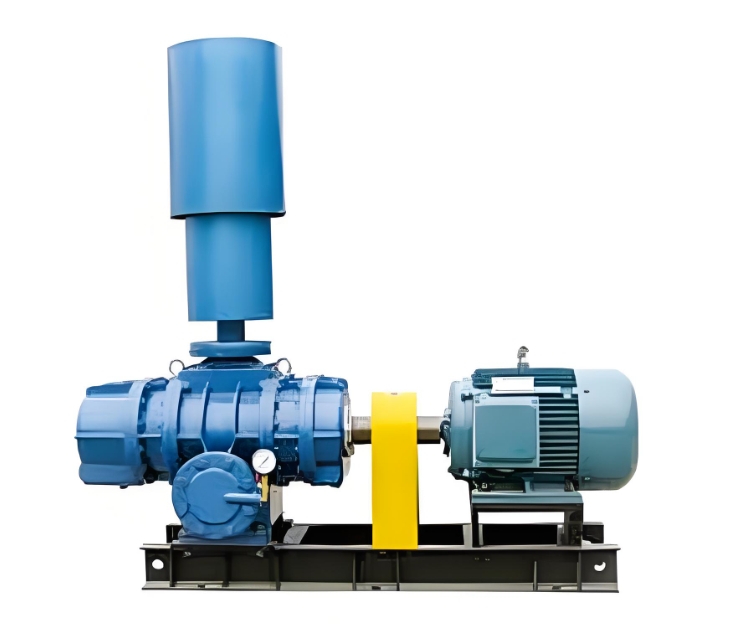
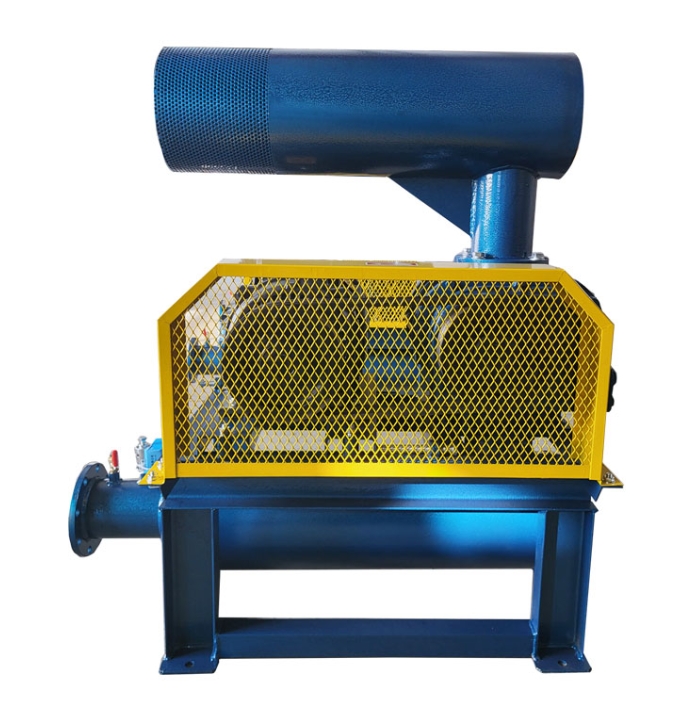
The sound insulation cover of Roots blower is a noise reduction device designed to address the high noise problem generated during the operation of Roots blower. Through comprehensive sound insulation, sound absorption, vibration isolation and other technical means, it effectively reduces the impact of equipment on the environment. The following is a detailed introduction:

1、 Core functions and noise reduction principles
Sound insulation and noise reduction
The soundproof hood encloses the entire fan and blocks the propagation of airborne sound through high-density materials (such as 2-3mm steel plates), combined with an internal sound absorbing layer (such as 50mm thick ultra-fine glass wool) to absorb reverberation sound energy, which can reduce noise by 15-30 decibels. For example, in a case of a sewage treatment plant, the noise level of the fan during bare operation reached 100dB. After installing a soundproof cover, it met the emission standards of ≤ 55dB during the day and ≤ 45dB at night.
Vibration isolation treatment
Install rubber or felt flexible connection layers between the soundproof enclosure, fan, and foundation to prevent equipment vibration from being transmitted to the enclosure through rigid connections and to prevent the enclosure from becoming a secondary sound source. For example, installing spring dampers or rubber isolation pads between the fan and the foundation can further reduce structural noise.
Ventilation and heat dissipation design
Mechanical ventilation is adopted, and an axial flow fan is installed at the top of the hood for forced ventilation. At the same time, a soundproof channel is set up at the air inlet to ensure the fan's heat dissipation needs and avoid new noise leakage. For example, in a certain case, the ventilation system was optimized to control the temperature inside the hood to ≤ 40 ℃.
2、 Structural Design and Material Selection
Wall material and damping layer
The cover body is made of 2-3mm steel plate and coated with a 7mm thick asphalt stone cotton wool damping layer on the surface to suppress resonance and reduce the fitting effect. The thickness of the damping layer should be at least three times the thickness of the steel plate, and it should be firmly adhered. For example, after testing, the average transmission loss of such structures can reach 34-45dB.
Acoustic layer configuration
Lined with 50mm thick ultra-fine glass wool (density 25kg/m3), with a sound absorption coefficient of ≥ 0.5, covering a frequency range of 125Hz~4kHz. For example, in the horizontal plane of the fan center, high-frequency noise (above 2kHz) can be reduced by 10-15 dB through sound-absorbing materials.
Hole and joint treatment
Install a sleeve at the through-hole of the transmission shaft, lined with sound-absorbing material, with a length of at least 15 times the width of the gap.
The seams of the cover and the doors and windows are sealed with latex strips, and the sound leakage is reduced by 20-25dB after the seams are compacted.
Install double rubber brushes at the inlet and outlet to ensure the passage of materials and suppress noise leakage.
3、 Application scenarios and advantages
Industrial scene adaptation
Widely used in high noise environments such as sewage treatment plants, cement plants, chemical plants, etc., especially suitable for noise reduction of equipment in noise sensitive areas such as office areas and residential areas. For example, after the renovation of the fan room in a cement plant, the noise level at the factory boundary decreased from 85dB to below 50dB.
Comprehensive benefits
Environmental benefits: reduce noise pollution, improve the working environment for workers, and reduce the risk of occupational diseases.
Economic benefits: Extend equipment lifespan and reduce downtime losses caused by noise complaints.
Social benefits: Assisting enterprises in passing environmental inspections and avoiding penalties for excessive emissions.
4、 Design points and precautions
Shape and Space Optimization
The contour of the cover should conform to the shape of the fan to reduce the radiation area; Surface design enhances stiffness and avoids standing wave effects caused by parallel cover walls. For example, using a hexahedral gradient structure can increase the low-frequency sound insulation by 5-8dB.
Low frequency noise control
For the low-frequency noise around 250Hz of Roots blower, a perforated plate composite structure (such as plywood+air layer+glass wool) can be used, and its resonance absorption peak can cover this frequency band. For example, in a certain case, by optimizing the sound absorption structure, the noise at 250Hz was reduced by 12dB.
Maintain convenience
Set up detachable observation windows, access doors, and movable cover plates for easy daily inspection and maintenance. For example, using double-layer soundproof glass observation windows ensures visibility and reduces sound leakage.