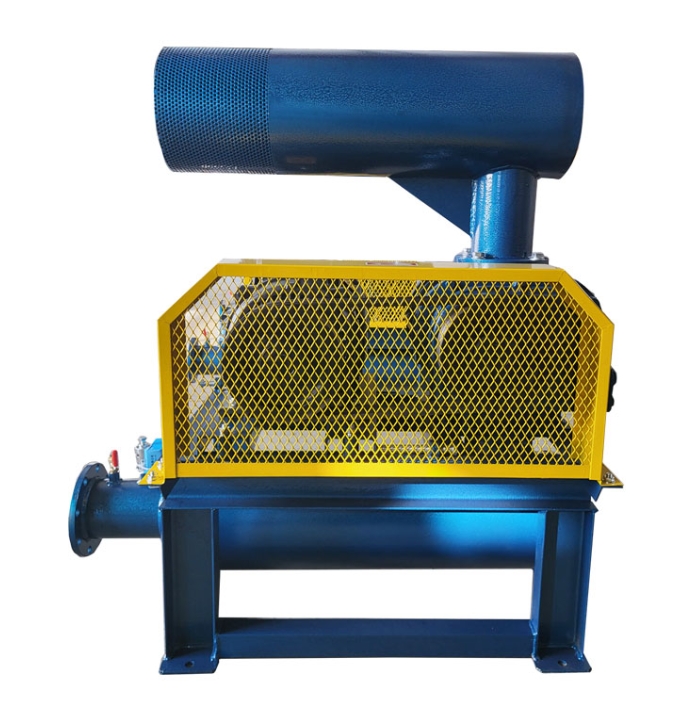
The 15kW Roots blower is a commonly used medium power model in the industrial field, characterized by stable flow rate, wide pressure range, and diverse applicable scenarios. The following analysis focuses on its core parameters, typical models, application scenarios, and selection recommendations:

1、 Core parameters
Flow range: There is a significant difference in flow rate among different models of 15kw Roots blowers, for example:
SR100 type: Under a pressure of 58.8kPa, the flow rate is 7.60-8.75m3/min; At a pressure of 44.1kPa, the flow rate can reach 8.98m3/min.
SR125 type: Under a pressure of 29.4kPa, the flow rate is 12.83m3/min; At a pressure of 58.8kPa, the flow rate is 7.64-9.15m3/min.
SR150 type: Under a pressure of 9.8kPa, the flow rate is 22.85-25.42m3/min; At a pressure of 39.2kPa, the flow rate is 10.86-13.70m3/min.
SR175 type: Under a pressure of 9.8kPa, the flow rate is 26.75-30.25m3/min; At a pressure of 19.6kPa, the flow rate is 22.13-29.94m3/min.
SR200 type: Under a pressure of 9.8kPa, the flow rate is 31.17-35.01m3/min; At a pressure of 19.6kPa, the flow rate is 30.54m3/min.
Pressure range: The pressure range of a 15kw Roots blower is usually 9.8kPa to 58.8kPa, and some models may have higher pressure ranges.
Speed range: The speed is usually between 990-1760rpm, with slight differences in speed among different models.
Motor power: 15kw, strong driving capability, can provide stable airflow output.
2、 Typical model
SR series:
SR100 type: suitable for small and medium-sized industrial scenarios, with low flow but high pressure.
SR125 type: With a wide range of flow and pressure, it is suitable for various working conditions.
SR150 type: High traffic, suitable for scenarios that require high traffic.
SR175 type: High flow and pressure, suitable for medium and high pressure conditions.
SR200 type: flow rate, suitable for large industrial scenarios.
Series:
-Type 100: Under a pressure of 58.8kPa, the flow rate is 6.53m3/min.
-Type 125: Under a pressure of 49kPa, the flow rate is 8.35-10.01m3/min; At a pressure of 58.8kPa, the flow rate is 6.9-9.13m3/min.
-125C type: Under a pressure of 29.4kPa, the flow rate is 14.85m3/min; At a pressure of 44.1kPa, the flow rate is 8.7-12.7m3/min.
-Type 150: Under a pressure of 9.8kPa, the flow rate is 22m3/min; At a pressure of 19.6kPa, the flow rate is 16.73-18.93m3/min.
-Type 175: Under a pressure of 9.8kPa, the flow rate is 26.75-30.25m3/min; At a pressure of 19.6kPa, the flow rate is 21.63-29.94m3/min.
-200B type: Under a pressure of 9.8kPa, the flow rate is 22.73-30.92m3/min; At a pressure of 14.7kPa, the flow rate is 22.42-30.43m3/min.
-Type 200: Under a pressure of 9.8kPa, the flow rate is 31.77-35.68m3/min.
3、 Application scenarios
Wastewater treatment: used in aeration tanks to provide sufficient oxygen for microorganisms, help decompose organic matter in wastewater, and purify water quality.
Aquaculture: By injecting air into the water through an aeration system, the dissolved oxygen content in the water is increased, providing a good living environment for aquatic organisms, promoting growth, and increasing aquaculture density and yield.
Material transportation: Used in industries such as chemical and building materials to transport powdered cement, flour, or granular plastics, grains, etc. Mixing materials with air through pipelines, utilizing the generated airflow pressure to transport materials to designated locations, achieving continuous and stable transportation.
Industrial combustion assistance: In cement production, as a combustion assistance fan, combustion gas is sent from the bottom of the kiln to help materials fall vertically inside the kiln, achieving the firing of clinker.
Homogenization warehouse mixing: The discharged compressed gas enters the material layer through the bottom inflation box of the warehouse, causing the material to fluidized and roll up and down, achieving a uniform mixing effect.
Fuel atomization: Used in tunnel ceramic kilns, vertical magnesia kilns, and glass pool furnaces to atomize fuel, dividing the oil flow into fine strands and trapping bubbles, forming a group of small diameter droplet mist.
Pneumatic ash conveying: In thermal power plants, ash is sent into the ash silo through compressed gas, or a vacuum pump is installed at the end of the ash discharge system to suck the gas in the pipeline and make it fall into the ash silo.
Promoting chemical changes: In the gas-solid two-phase contact of chemical changes, the compressed gas provided causes solid particles to float and fluidized, fully contacting with other products or catalysts, thereby improving the speed and efficiency of the reaction.
Vacuum cleaning: Use a hose suction head to clean the dust on the pot body and platform, and use a vacuum pump to extract the gas from the dust and clean various loose particles and dust.
Incinerator air supply: In the incinerator, fuel is sent into the combustion chamber through compressed gas to achieve high-temperature incineration.
4、 Selection suggestions
Select based on operating conditions:
Low pressure and high flow rate: Choose models with higher flow rates, such as SR150, SR175, and SR200.
High pressure and low flow: Choose models with higher pressure, such as SR100 and SR125.
Flow redundancy design: In actual selection, the flow should be slightly higher than the required value (usually leaving a margin of 10-20) to cope with changes in system resistance.
Brand and after-sales service: Famous brands often have higher prices, but their quality and after-sales service are more guaranteed.
Material selection: Fans made of different materials have varying durability and performance, resulting in differences in price. It is necessary to choose the appropriate material based on actual working conditions.