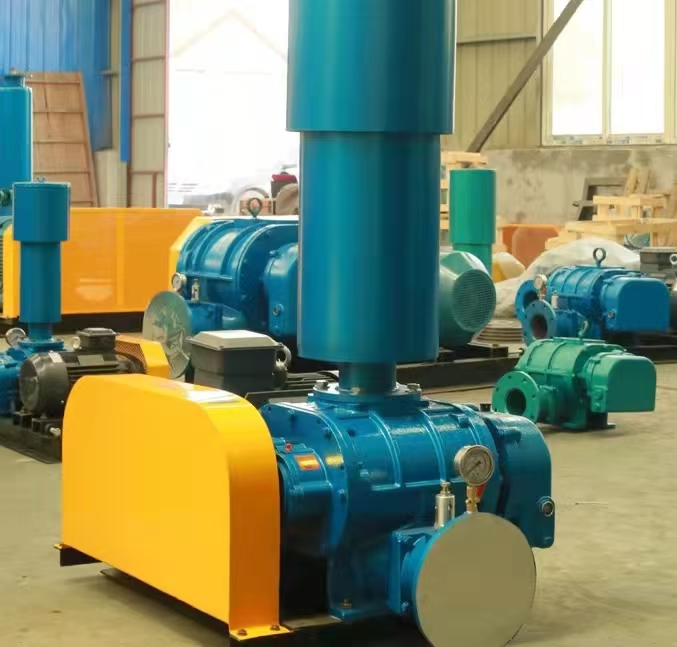
Roots blower and centrifugal blower are two different types of fans, with significant differences in their working principles, structural characteristics, performance parameters, and application scenarios. The following is a detailed comparative analysis:
---

**1、 Comparison Table of Core Differences**
|* * Comparison item * * | * Roots blower * * | * * Centrifugal blower * *|
|------------------|----------------------------------|----------------------------------|
|* * Working principle * * | Volumetric (forced delivery of gas through impeller engagement) | Kinetic (acceleration of gas through impeller centrifugal force)|
|* * Flow pressure characteristics * * | Constant flow rate, pressure changes with system resistance | Significant flow rate changes with pressure (with working curve)|
|Efficiency range * * | 60-75 | 70-85 (wider zone)|
|* * Pressure * * | Up to 98kPa (0.98bar) | Typically ≤ 30kPa (0.3bar)|
|* * Flow regulation * * | Variable frequency or bypass regulation required | Flexible adjustment through inlet guide vanes/variable frequency|
|* * Structural Features * * | Double bladed wheel+synchronous gear, clearance | Single bladed wheel+volute, contactless sealing|
---
**2、 Differences in working principles**
**1. Roots blower (positive displacement)**
-* * Working process * *:
Two three or two bladed rotors rotate in opposite directions inside the casing, achieving gas delivery by periodically changing the chamber volume.
```mermaid
graph LR
A [intake] -->B [rotor meshing forms a closed cavity]
B -->C [Decreased cavity volume]
C -->D [Gas forced out]
```
-* * Features * *:
-The flow rate is proportional to the rotational speed and is almost unaffected by pressure
-The outlet pressure is determined by the system back pressure
**2. Centrifugal fan (kinetic energy type)**
-* * Working process * *:
The rotation of the impeller gives kinetic energy to the gas, and the volute converts the kinetic energy into static pressure energy.
```mermaid
graph LR
E [Axial intake] -->F [Centrifugal acceleration of impeller]
F -->G [snail shell expansion]
G -->H [High pressure discharge]
```
-* * Features * *:
-Pressure flow follows a parabolic relationship (effective point)
-There is a risk of surge (to avoid unstable operating conditions)
---
**3、 Performance Curve Comparison**
|* * Features * * | * Roots blower * * | * * Centrifugal blower * *|
|----------------|------------------------------|------------------------------|
|* * Flow curve * * | Approximate vertical line (constant flow) | Parabola (flow rate varies with pressure)|
|Efficiency curve * * | relatively flat (60-75) | spike shaped (narrow region)|
|Overload capacity * * | Can operate under short-term overpressure | Overpressure can cause surge|
---
**4、 Select application scenarios**
**Priority selection of Roots blower**
1. Constant flow conveying is required (such as pneumatic conveying, backwashing)
2. High pressure and low flow conditions (>30kPa and<50m3/min)
3. The medium contains * * dust or particulate matter * * (with better wear resistance design)
4. In situations where a simple and easy to maintain structure is required
**Priority selection of centrifugal fans**
1. * * High flow medium low pressure * * demand (such as ventilation, boiler induced draft)
2. Continuous operation system that requires * * energy-saving * *
3. Environment sensitive to noise (centrifugal fans are quieter)
4. In situations where the operating parameters * * fluctuate greatly * *
---
**5、 Maintenance and Cost Comparison**
|* * Project * * | * Roots blower * * | * * Centrifugal blower * *|
|---------------|---------------------------|---------------------------|
|* * Maintenance frequency * * | Change gear oil every 2000 hours | Check bearings every 5000 hours|
|* * Vulnerable parts * * | Synchronous gears, shaft seals | Bearings, impeller dynamic balancing|
|* * Life cycle * * | 5-8 years (impeller repairable) | 8-12 years (overall replacement)|
|* * Purchase cost * * | Low (20-30% cheaper for the same power) | High|
|* * Operating cost * * | High (low efficiency) | Low (energy-saving zone)|
---
**6、 Common Misunderstandings Clarification**
1. * * Misconception * *: "Roots blower is a type of centrifugal blower"
-Fact: Both belong to volumetric and kinetic fans, with different principles
2. * * Misconception * *: "Roots blower has lower efficiency than centrifugal blower"
-Fact: Under low flow and high pressure conditions of less than 30m3/min, Roots blower efficiency may be higher
3. * * Misconception * *: "Centrifugal fans cannot be used for pneumatic conveying"
-* * Fact * *: Specially designed centrifugal fans (such as multi-stage boosting) can also be used for conveying
---
**7、 Technology integration**
1. Magnetic levitation Roots blower:
-Combining magnetic levitation bearing technology to eliminate gear transmission
-Efficiency has been improved to over 80 (traditional Roots blower is about 65)
2. * * High speed centrifugal blower * *:
-Adopting a ternary flow impeller, the pressure can reach 50kPa
-Replace Roots blower in some fields (such as sewage treatment)
---
**Summary and Suggestions**
-* * Selection principle * *: Select the type of fan based on the * * system resistance curve * *
-* * Key judgment points * *:
-Need constant flow → Choose Roots
-Need to change flow rate → choose centrifuge
-* * Special working conditions * *:
-Dust containing gas → Roots (more mature wear-resistant design)
-High flow rate of clean air → centrifugation
For specific selection support, please provide:
① Required flow range ② System pressure requirements ③ Medium characteristics (temperature/humidity/dust content)