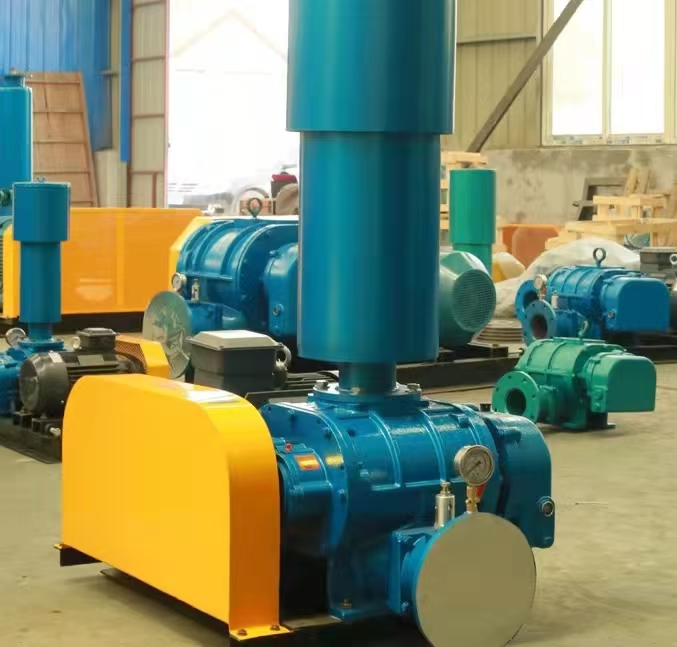
**Detailed explanation of the working principle of Roots blower**
Roots blower is a type of volumetric gas conveying equipment, whose core principle is to use two interlocked impellers to rotate in a closed chamber, forcibly pushing the gas to achieve directional conveying. The following is a step-by-step analysis:
---

**1、 Core work process**
1. * * Inhalation stage**
-When the impeller (rotor) separates from the inlet, the chamber volume increases → negative pressure is formed → gas is sucked in.
-* Key point *: The air inlet has no valve and is directly sucked in by volume changes.
2. * * Closed conveying stage**
-The impeller continues to rotate, enclosing the gas within the chamber formed by the impeller and the casing.
-Characteristic: The gas is not compressed and only moves in position (pressure does not increase temporarily).
3. * * Exhaust Stage**
-When the impeller is connected to the exhaust port, the chamber volume decreases and the gas is forced out.
-Pressure generation: The exhaust pressure is determined by the resistance of the backend system (such as pipeline and valve resistance).
```plaintext
[Schematic diagram of work cycle]
① Inhalation → ② Closure → ③ Exhaust → Recirculation
```
---
**2、 Core structure function**
|* * Component * * | * * Function * *|
|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|* * Impeller * * | Two blade or three blade rotor, precision machined (clearance 0.15~0.4mm), forced to push gas|
|* * Synchronous gear * * | Ensure non-contact meshing of the two impellers (phase difference of 180 °) to avoid collision|
|* * Chassis * * | Enclosed cavity, capable of withstanding pressure (made of cast iron/stainless steel material)|
|* * Import and Export * * | Unidirectional airflow design to prevent backflow|
---
**3、 Key characteristics**
1. * * Volumetric principle**
-The flow rate is strictly proportional to the speed (* * constant current characteristic * *), and the flow rate remains almost unchanged when the pressure changes.
-Formula *:` Q=4 × V × n × η ` (V: impeller displacement, n: Rotational speed, η: Volumetric efficiency).
2. * * No internal compression**
-The gas in the chamber is not actively compressed, and the pressure increase is only caused by exhaust resistance.
-Result: The efficiency is lower than that of screw machines, but the structure is simpler and more reliable.
3. * * Forced delivery**
-Even if the outlet pressure fluctuates (such as pipeline blockage), the flow rate can still be maintained stable (overpressure prevention is required).
---
**4、 Performance curve**
|* * Parameters * * | * Roots blower * * | * * Comparison centrifugal fan * *|
|----------------|--------------------------------|-----------------------------|
|Flow pressure relationship | Horizontal curve (constant flow) | Steep drop curve (pressure ↑ flow ↓)|
|Efficiency | 50-70 (optimal in the medium and low pressure range) | 60-85 (narrow range)|
|Applicable pressure | ≤ 98 kPa (conventional) | Wide range (up to several hundred kPa)|
---
**5、 Application examples**
1. * * Sewage treatment aeration**
-The impeller rotates at 1450 rpm and delivers air to the aeration tank at a constant pressure of 49 kPa.
2. * * Pneumatic conveying**
-Push granular materials (such as flour, cement) at a pressure of 58.8 kPa.
3. * * Vacuum adsorption**
-When used in reverse connection, it serves as a vacuum pump (negative pressure -50 kPa) for suction cup handling.
---
**6、 Frequently Asked Questions**
**Q: Why is the noise of Roots blower loud**
-* * Reason * *: Airflow pulsation (more pronounced in the two blade type) and gear meshing impact.
-Solution: Choose a three leaf type, add a muffler or soundproof cover.
**Q: How to regulate traffic**
-* * Correct method * *: Variable frequency speed regulation (adjusting speed).
-* * Incorrect method * *: Turn down the outlet valve (which may cause overpressure damage!).
---
**Summary: Roots blower forcibly delivers gas through impeller engagement, suitable for low-pressure constant flow scenarios. It has the advantages of simple structure and durability, but attention should be paid to pressure limitation and noise control.